(文献综述)Planning with preference
Jorge A. Baier et al., AI 2008
-
Progress: 20%, link
-
Terms:
-
Preference-based planning (PBP)
-
主要调研了两个问题:
- 如何在PBP的框架下定义preference。(planning preference languages) 需要一种语言来定义preference,建立起用户的preference和规划的preference的联系 1. 如何定义preferences 2. Aggregate不同的preference
- 定义了preference后,如何有效的优化出preferred plan。(algorithms for planning with preferences)
-
传统规划与PBP(如何以preference作为依据比较plan?)
,状态,初始状态,目标( )和算子(operators) - 传统方法: STRIPS,ADL,PDDL(主流方法)。
- PBP:
用以表示依据preference对plan的比较( , is at least preferred as plan ),更严格的用 - 部分(partial)/全部(total)preference
-
Preference languages and formalisms(如何定义)
- 需要考虑的点:
- 普适性(compact, not explicitly)
- (Over states) referring to properties of a plan.
- (Over actions) Additionally provide for preferences over actions occurrences, 以附加在action上为主,也会部分的附加在state上。
- Quantitative or qualitative or both
- Quantitative languages: solutions are associated with numeric values
- Decision-Theoretic Planning (DTP)
- Partial Satisfaction Planning (PSP)
- PDDL3 Linear temporal logic involves here.
- Qualitative languages: 不需要依据任何数据进行定义
- Languages Based on Ranked Knowledge Bases(Languages based RKB)
- Conditional Preference Networks (CP nets, Boutilier et al.) 扩展形式,引入了trade-offs:TCP-nets
- Temporal and Temporally Extended Preferences
- Both:
- 其它方法LLP,DT-Golog
- Quantitative languages: solutions are associated with numeric values
- 最近的解决方案PDDL3,planning with hierarchical task networks (HTN)
- 需要考虑的点:
-
PBP算法(如何求解)
- Optimal, k-optimal, Incremental
- Search-Based PBP
- PREF-SEARCH
- Final State Preferences
- Temporally Extended Preferences (TEPs)
- PPLAN
- HPLAN-P
- SGPlan5
- PBP through general-purpose solvers
-
研究方向
- 效率问题。现在的PBP planner的效率主要依赖于relaxed planning graph techniques,在简单场景中信息不足(?)
- 现阶段主要研究集中在detereminstic planning上。缺少对incomplete knowledge等情景的研究
- 现阶段的解法需要preference elicitation已解决,但这点在实际问题中较难达成。以decision-making的形式获取user preference比较困难。一种解决的方向是用交互的方式develop a most-preferred plan。
A prior preference-based decision-making algorithm in Pareto Optimization
Masoumeh Jafari et al., ICCKE 2019
-
Progress: 20%, link
-
主要工作
- 对于multi-objective optimization(MOO)问题:
将objectives用Favorite Region(FR)表达,引入Angle-based updating Pareto front (PF) 算法中
- FR(Favorite Region)基于objective space创建(将FR和angle-based引入PF问题)
- PF的解在演进的过程中趋近于FR(要优化的会变得更好,不重要的也不会丢掉)
- 不在FR中的解也不会消失(go away)。解的fronts level(?)会随着变化?
- 如何平衡了适当的解的exploration和exploitation(均匀分布)?undesirable region中的解的密度也未受影响
- 实验
问题: PF是什么?FR是什么?angle-based是什么?first and second frtons是什么?
- Pareto optimal solutions:不是单一最优全局解,而是一组trade-off解(Pareto optimal set)
- Pareto optimal set’s image of the objective space is Pareto optimal front
- E.g.:
- f1, f2: objectives space
- non-dominance solutions sorted in first, second Pareto front
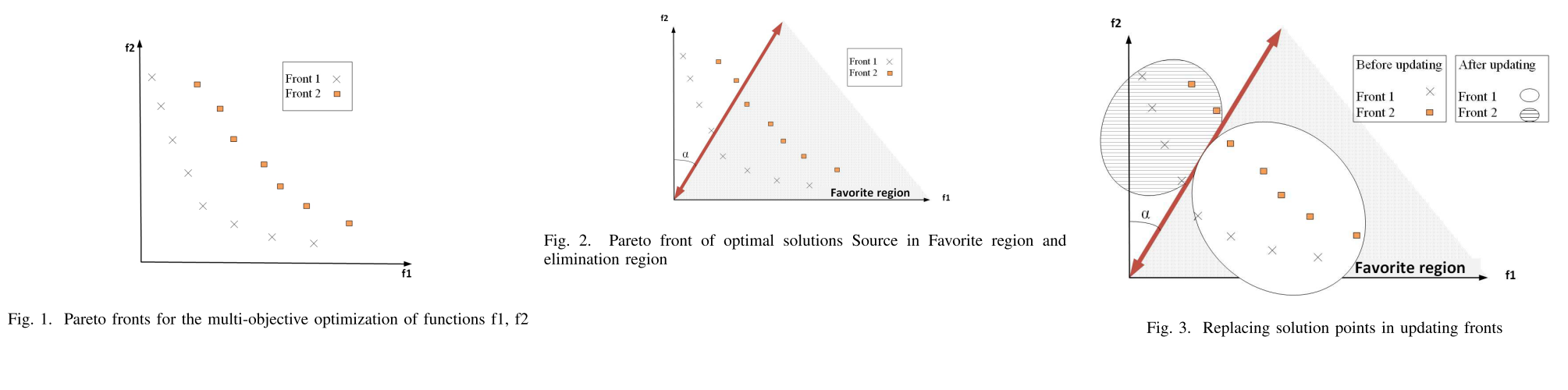
- Decision making(DM) 两类MOO算法:No-preference和Preference-based 三种方法利用preference:(前两个是什么?最后一个好理解) 1. Priori method 2. Posteriori method(本文重点) 3. Interactively method
- 对于multi-objective optimization(MOO)问题:
将objectives用Favorite Region(FR)表达,引入Angle-based updating Pareto front (PF) 算法中
-
Method:
- 旋转向量将Front 1 和Front 2进行划分
- 划分区域即为favorite region和elimination region
- 根据向量划分结果将favorite region内的解放入Front 1中,将elimination region中的解放入Front 2中
- 重复上述过程直至收敛或停止条件
-
ref